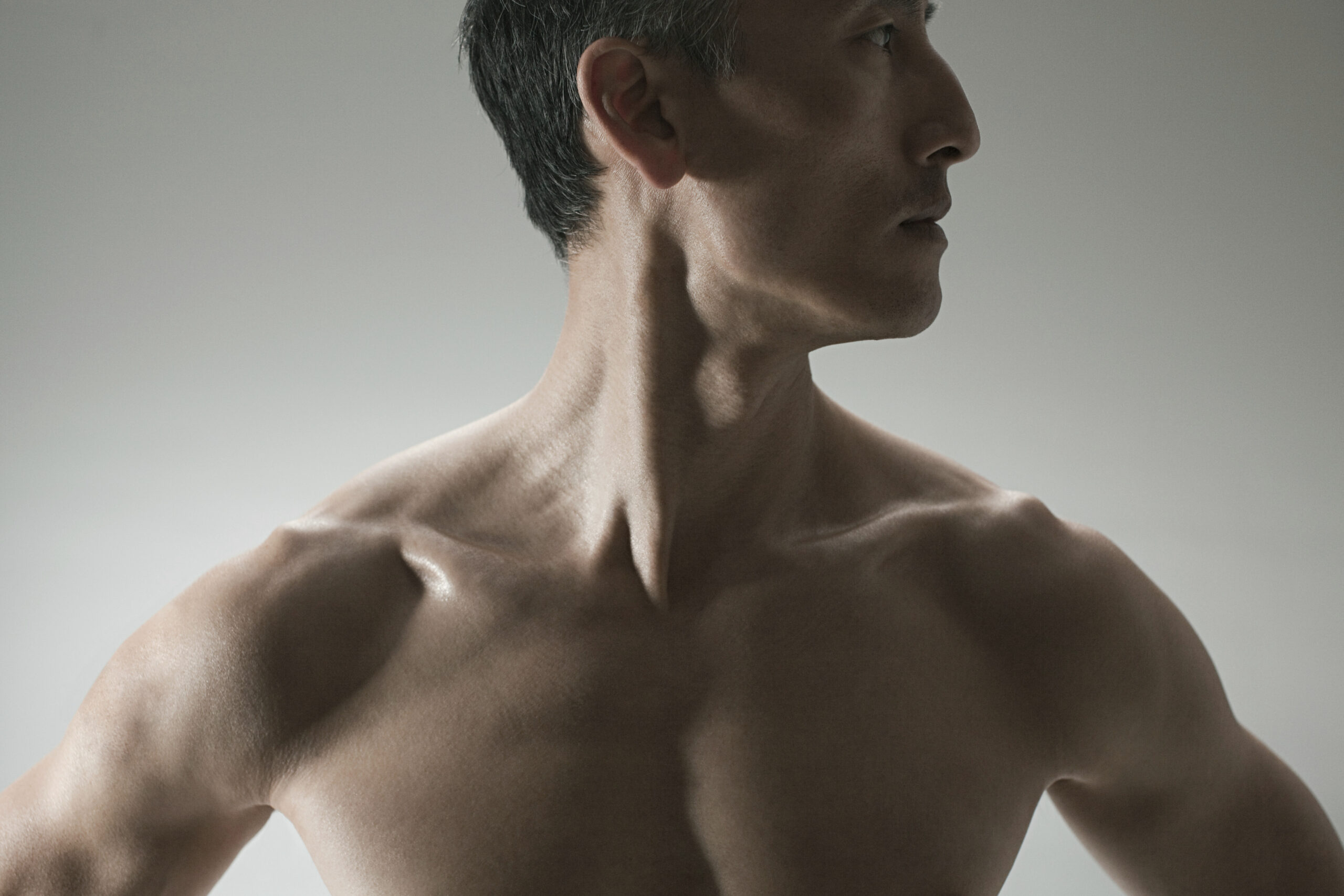
The sternocleidomastoid (SCM) is a crucial muscle in the neck, playing a key role in head movement and posture. Problems with this muscle can lead to discomfort and noticeable posture imbalances. Understanding how to examine your sternocleidomastoid muscle for issues can help you pinpoint potential causes of neck pain, headaches, or other related symptoms. This guide will provide a detailed breakdown of methods to identify problems with your sternocleidomastoid muscle.
What is the Sternocleidomastoid Muscle?
The sternocleidomastoid muscle is a prominent structure that extends from the base of your skull, just behind and below your ear, down to the collarbone (clavicle) and sternum. Its primary functions include:
- Rotation of the head: Turning your head side-to-side.
- Flexion of the neck: Bringing your head down towards your chest.
- Postural support: Helping maintain alignment of the head and neck.
When functioning normally, the SCM contributes to smooth head movements and balanced posture. However, tension or dysfunction in this muscle can result in discomfort, stiffness, and noticeable misalignment.
Signs Your Sternocleidomastoid Might Be a Problem
Several indicators suggest that your sternocleidomastoid muscle may be contributing to discomfort or functional issues. Here are two main ways to identify potential problems:
1. Observing Postural Alignment in the Mirror
One of the simplest ways to identify issues with your SCM is to observe your head and neck position in the mirror. Look for the following:
- Head Tilt: Is your head tilted slightly to one side? A tight SCM can pull the head towards the affected side.
- Rotation: Does your head appear rotated? If one SCM is tight, it may cause your head to rotate in the opposite direction.
- Repeated Patterns in Photos: If you often notice a tilted or rotated head in photos, this could indicate an ongoing issue with your SCM.
For example:
- A tight right SCM may pull your head to the right while rotating it to the left.
- Similarly, a tight left SCM can cause the head to tilt left and rotate right.
Even subtle asymmetries in your head position could signify underlying muscle tension or dysfunction.
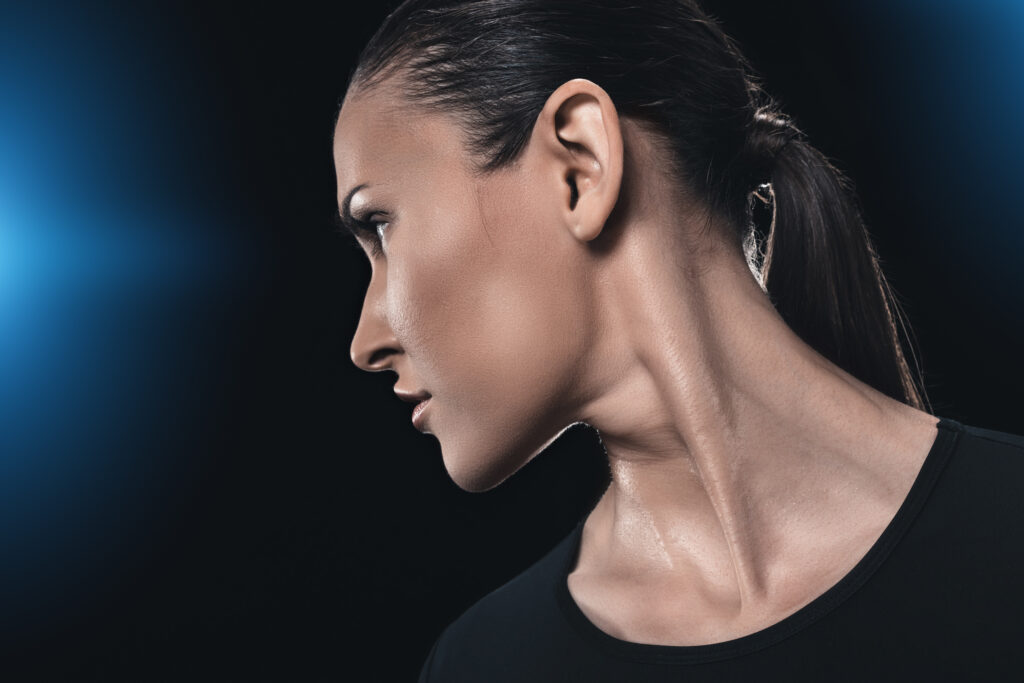

2. Palpating the Sternocleidomastoid Muscle
Touching and feeling the SCM can also provide clues about its condition. Follow these steps to assess your muscle:
- Locate the Muscle:
- Start by feeling the bony area behind and below your ear.
- Follow the muscle as it travels diagonally down the side of your neck, attaching to your collarbone and sternum.
- Check for Tenderness:
- Gently press along the length of the muscle.
- Compare both sides of your neck. Does one side feel tender or more sensitive than the other? This tenderness could indicate tension or irritation.
- Strum Across the Muscle:
- Use your fingers to gently “strum” across the muscle fibers.
- Note whether one side feels tighter, thicker, or more rope-like compared to the other.
- Reproduce Symptoms:
- Pressing on trigger points in the SCM may replicate discomfort, such as pain in the head, neck, or even behind the eye. This referral pattern is a common symptom of SCM dysfunction.
By palpating your SCM, you can gather valuable information about potential asymmetries, tension, or irritation in the muscle.
Common Symptoms of Sternocleidomastoid Dysfunction
Problems with the sternocleidomastoid can manifest in various ways, often beyond the neck itself. Symptoms may include:
- Neck Pain or Stiffness: Localized discomfort in the neck, especially when turning your head.
- Headaches: Pain that radiates from the base of the skull to the forehead or behind the eye.
- Postural Imbalance: A visible tilt or rotation of the head.
- Referred Pain: Discomfort that extends to the shoulder, upper back, or jaw.
These symptoms can stem from tightness, trigger points, or overuse of the SCM, often aggravated by poor posture, stress, or prolonged sitting.
Why Does the Sternocleidomastoid Muscle Become a Problem?
Several factors can contribute to SCM dysfunction:
- Poor Posture: Slouching, forward head posture, or looking down at screens for extended periods.
- Stress: Emotional tension can cause the SCM to tighten, leading to discomfort.
- Repetitive Strain: Activities like prolonged phone use (holding a phone between your ear and shoulder) or one-sided head movements.
- Injuries: Whiplash or other neck trauma.
Understanding these causes can help prevent further strain and guide treatment strategies.
What to Do If You Suspect SCM Issues
If you notice signs of SCM dysfunction, there are steps you can take to alleviate discomfort and restore function:
1. Stretching and Relaxation
Gentle stretches targeting the SCM can help release tension:
- Tilt your head to one side while gently pulling it towards your shoulder with your hand.
- Rotate your head in the opposite direction to stretch the SCM on the affected side.
2. Self-Massage
Using your fingers, apply gentle pressure along the length of the muscle to release tension and improve circulation.
3. Postural Corrections
Be mindful of your posture, especially during desk work or screen time. Keep your head aligned with your spine and avoid slouching.
4. Professional Help
If self-care techniques don’t resolve your symptoms, consider consulting a physical therapist or massage therapist for targeted treatment.
Conclusion
The sternocleidomastoid muscle is a vital structure that impacts head movement, posture, and overall neck health. By observing your posture and palpating the muscle, you can identify potential issues and take steps to address them. Regular self-care, proper posture, and professional assistance can help ensure your SCM remains healthy and functional, reducing the risk of discomfort and improving your quality of life.
Also Read: How to Treat Sternocleidomastoid Muscle Tension
About:
I’m Hina Sheth. I have been treating complex orthopedics, sports and pelvic floor physical problems for over 25 years with amazing results. Now I want to bring my knowledge to the global community so I can spread my knowledge to you.
Our bodies are complex systems of 600 muscles and organs intertwined in a fascial system that all work together. Imbalances in this system such as trigger points, visceral and myofascial restrictions can lead to joint, pelvic, and organ issues.
Factors like nutrition, exercise, sleep, and stress play a crucial role. Unfortunately, our current healthcare model does not look at our bodies as a whole and oftentimes compartmentalize musculoskeletal injuries and dysfunctions.
At Rebalance, our goal is to holistically treat this complex system to restore harmony in the body. By addressing these imbalances, we help clients improve their overall health and well-being. Our vision is to empower individuals to create a healthier lifestyle for themselves.